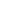
Are sea levels rising the same all over the world, as if we're filling a giant bathtub?
No. Sea level rise is uneven, the two main reasons being ocean dynamics and Earth’s uneven gravity field.
First, ocean dynamics is the redistribution of mass due to currents driven by wind, heating, evaporation and precipitation. For example, during La Niña events, sea level goes down because some rain that usually occurs over the ocean shifts to land, and the same phenomenon produces low latitude currents that redistribute seawater. Regional climate cycles, like El Niño and La Niña, and longer-term effects, like the Pacific Decadal Oscillation, change ocean circulation, which changes sea level.
Second, because the distribution of Earth’s mass is uneven, Earth’s gravity is also uneven. Therefore, the ocean’s surface isn’t actually a perfect sphere or ellipsoid; it is a bumpy surface. As the land-based ice sheets of Greenland and Antarctica continue to unload their mass (lose ice) from far above sea level and far from the tropics, that mass reaches the sea in the form of meltwater that is then redistributed along Earth’s gravity field.
The areas farthest from the melted ice will see the most sea level rise as a result. Conversely, areas nearest to Greenland and Antarctica will see the least amount of sea level rise (and some areas will actually see sea levels drop). Scientists even track the annual cycle of ice sheet mass losses to further refine their sea level rise measurements.
Between 1993 and 2018, sea level rose 12 to 15 millimeters per year (about half an inch per year) in some regions, and went down by that amount in others. But on average, it has gone up by about 3 millimeters per year (about 28 millimeters, or 1-1/8 inches, per decade) in that same period. Most of this unevenness is caused by ocean dynamics.